Diagnosis of swollen gum abscess
Gum abscess is also known as a gingival abscess. In general, an abscess is an infection caused by bacteria.
Definition
Gum abscess is also known as a gingival abscess. In general, an abscess is an infection caused by bacteria. This bacterial infection causes inflammation and forms a cavity in the gums that contains pus or pus.
This kind of abscess can actually occur in all organs of the body. Starting from the oral cavity, vagina, armpits, anus to the spine. While gum abscess is one of five types of abscess caused by teeth. Other types of abscess are periapical abscess and abscess within the tooth itself.
A gum abscess is located below the gum line and forms a lump.
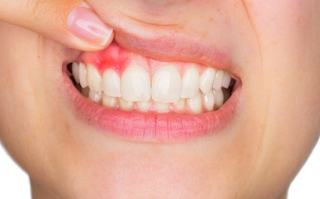
Reason
There are many things that can cause a gum abscess. Some of them are due to bacterial infections that come from cavities, brushing your teeth too hard, broken teeth, food scraps stuck in your gums or bleeding gums.
In addition, injuries from accidents and even excessive pressure on the dental brackets can also cause gum abscesses. In fact, according to research, the habit of children who often bite their fingers can cause gum abscesses.
Symptom
Usually a gum abscess will cause a throbbing pain in the infected area and feel very sensitive. Sufferers will experience various complaints ranging from mild pain, then getting sick, then turning into severe pain in a short time. The gums around the infected tooth will appear swollen even to the cheek area.
If the gum abscess is not treated, the infection can spread to penetrate the jawbone and cause swelling around the tissue. At this stage the patient will be seen experiencing swelling of the face. The face will look asymmetrical and there will be swelling of the glands in the neck area.
The infection can sometimes also spread to the wider surrounding tissue. This can cause permanent damage to the tissue around the tooth.
In severe stages, gum abscess can trigger nausea, vomiting, , and difficulty swallowing. Other symptoms that can also accompany are and mouth feels bad.
Diagnosis
Gum abscess can be identified through a thorough dental and oral examination. Usually, patients with gum abscesses only get checked out after the abscess they experience is in an intermediate stage and can't be treated with simple home treatments.
Through a complete examination, the dentist can determine if the condition has the potential to be something more serious or not. In addition, it can also be known if the condition requires an invasive procedure or only requires drug therapy.
Care
Very mild gum abscesses can be treated easily. Enough with an ice pack, giving painkillers, and can be added to gargling warm salt water. In some cases, gum abscesses can burst on their own without causing any pain.
Gum abscesses that are more severe and have occurred repeatedly require treatment with antibiotics and pain medication. If the condition of the gum abscess worsens, the doctor will usually recommend several treatment steps.
One of them is the act of removing pus from the abscess. This step can be done by giving an anesthetic injection by a dentist.
It is not recommended to do this at home for safety and hygiene reasons. Trying to do it yourself at home is prone to damage the surrounding tissue and make the inflammation of the gum abscess worse.
Another step that can be done in very severe conditions is to extract the tooth affected by the abscess. This is intended so that the infection does not spread to other teeth and also as access to discharge pus.
Prevention
In principle, the best way to treat an abscess is to prevent it from developing in the first place. You can take the following steps:
- Do regular checkups and cleaning tartar to the dentist every six months.
- Adopt a healthy habit of brushing your teeth twice a day. This will prevent food residue from sticking to the teeth for too long or in the gaps between the teeth.
- If you find a lump on the gums that doesn't go away within three days, you should immediately consult a dentist. Don't delay until things get worse.